Imagine a therapy that targets aging at the cellular level, recharges energy production, and supports longevity. That’s what NAD⁺ therapy promises. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) is a molecule essential for life, yet its levels decline as we age. Research shows this decline impacts metabolism, DNA repair, and resilience, leaving us more vulnerable to fatigue and age-related conditions.
What if the key to energy, clarity, and longevity was already inside your cells? Restoring NAD⁺ has emerged as a promising way to boost energy and longevity. Vita Bella’s NAD⁺ therapy restores this vital molecule to help you feel vibrant again.
Understanding NAD⁺: The Energy Currency of Cells
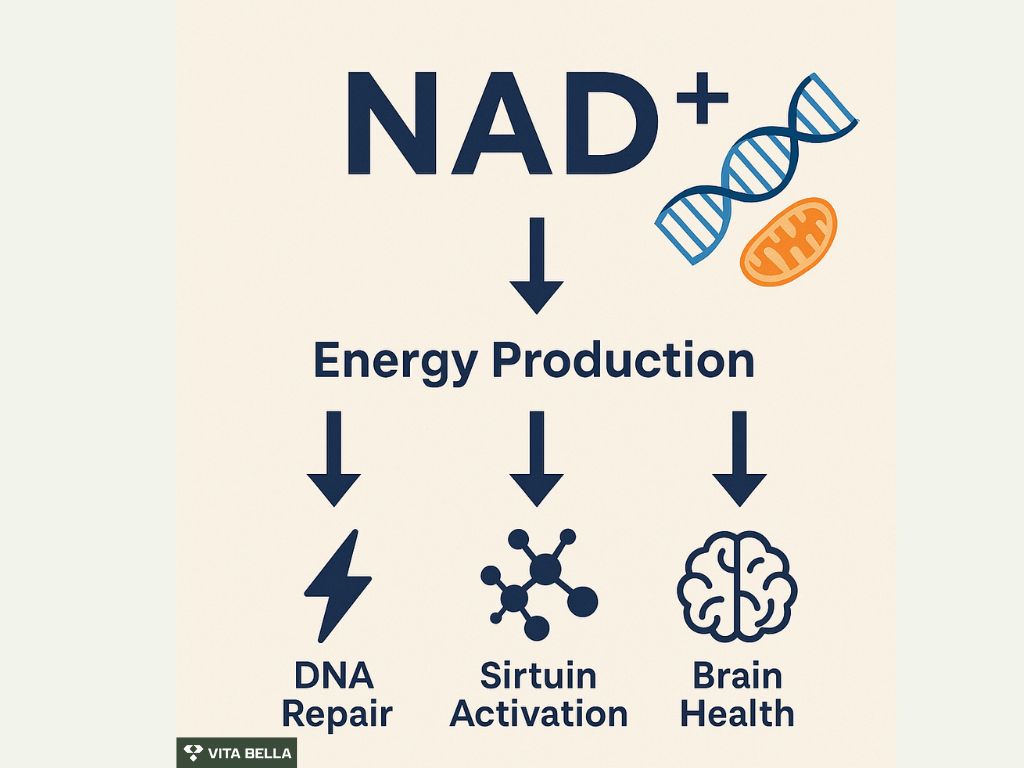
NAD⁺ functions 1 as a coenzyme in redox reactions, fueling mitochondrial ATP production. It also activates enzymes like sirtuins and PARPs that govern DNA repair, gene expression, and stress resistance.
Aging reduces NAD⁺ significantly. One review 2 found that levels in human tissues can drop by as much as 50% between early adulthood and old age, which correlates with higher oxidative stress and cellular dysfunction. This makes NAD⁺ 3 replenishment a cornerstone of regenerative medicine.
How NAD⁺ Therapy Works
By increasing NAD⁺ availability, therapy provides cells with the fuel they need to function optimally. Higher NAD⁺ levels enhance mitochondrial energy production, activate longevity-related enzymes like sirtuins, and support DNA repair. Together, these effects strengthen multiple systems from metabolism to brain health helping the body perform more efficiently and age more gracefully.
Mitochondrial energy: More NAD⁺ means more efficient ATP generation. In preclinical studies 1, NAD⁺ restoration improved energy metabolism and reduced fatigue symptoms.
DNA repair: NAD⁺ fuels PARPs, key for repairing strand breaks. Experimental data 2 show up to a four-fold increase in DNA repair efficiency when NAD⁺ levels are optimized.
Longevity pathways: Sirtuins, which depend on NAD⁺, regulate metabolism and aging. Higher NAD⁺ has been linked to increased lifespan in studies 3 by as much as 15–20%.
Neuroprotection: A study 4 shows that in models of cognitive decline, NAD⁺ replenishment preserved synaptic function and slowed neuron loss.
Clinical Applications of NAD⁺ Therapy
NAD⁺ therapy could play a neuroprotective role, helping preserve cognition, focus, and mental clarity as we age. By optimizing mitochondrial function, NAD⁺ therapy supports healthy weight control and may reduce risks associated with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
1. Anti-Aging and Regeneration
NAD⁺ decline is a well-recognized hallmark of aging. Lower levels impair mitochondrial efficiency, reduce DNA repair, and weaken the body’s resilience against stress. By boosting NAD⁺, therapy directly restores mitochondrial health and supports cell survival. In one clinical trial 5, supplementation with NAD⁺ precursors led to over a 40% rise in whole-blood NAD⁺ within just 2 weeks, accompanied by measurable improvements in metabolic health.
2. Metabolic Health
Metabolic disorders like obesity, insulin resistance, and fatty liver disease are increasingly linked to cellular energy deficits and oxidative stress. NAD⁺ plays a central role in regulating glucose metabolism, fatty acid oxidation, and insulin sensitivity. Research 6 explains that elevating NAD⁺ improves glucose tolerance and reduces fat accumulation by 30%, showing how therapy can rebalance metabolism.
3. Cognitive Support
The brain consumes large amounts of energy, making it highly dependent on NAD⁺ for neuronal survival and plasticity. As NAD⁺ declines with age, neurons become more vulnerable to oxidative stress and degeneration. Preclinical studies 4 in Alzheimer’s disease models show that restoring NAD⁺ not only improves memory performance but also reduces harmful beta-amyloid buildup, a key feature of the disease.
4. Muscle and Endurance
Muscle weakness and fatigue are common consequences of NAD⁺ depletion. Since mitochondria power muscle contraction, insufficient NAD⁺ reduces endurance and recovery capacity. In studies 7, replenishing NAD⁺ restored muscle function to youthful levels and increased endurance by over 50%. This means NAD⁺ therapy may not only improve daily energy but also help athletes, older adults, and those in rehabilitation programs regain stamina and strength.
Safety and Tolerability of NAD⁺ Therapy
Current data from clinical trials 3 show NAD⁺ therapy and its precursors are safe and well-tolerated. Reported side effects are mild and temporary, such as flushing or digestive discomfort. Importantly, to date, it has reported no severe adverse events, supporting its use under medical supervision.
Practical Usage and Lifestyle Synergy
Delivery methods include intravenous infusions, subcutaneous injections, and oral precursors like nicotinamide riboside. Many protocols start with a loading phase followed by maintenance.
To amplify benefits, NAD⁺ therapy pairs well with:
Exercise, which naturally stimulates NAD⁺ synthesis
Intermittent fasting or caloric restriction, proven to activate NAD⁺ pathways
Nutrient-rich diets, especially those high in tryptophan and niacin
These lifestyle approaches can boost therapy’s impact and sustain long-term cellular health.
Vita Bella Knows the Science of Staying Strong
Energy dips, brain fog, and muscle fatigue are not just “getting older”; they’re signals your cells are running low on NAD⁺. This natural decline weakens repair, performance, and resilience.
Vita Bella brings you cutting-edge NAD⁺ therapy designed to restore balance at the cellular level. With science on your side, you can power through life with strength, clarity, and confidence.
FAQs
What is NAD⁺ therapy?
NAD⁺ therapy is a treatment that replenishes nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a molecule essential for energy production, DNA repair, and healthy aging. By restoring this vital coenzyme, the therapy helps reverse some of the natural cellular decline linked to aging.
How does NAD⁺ therapy improve health?
By restoring NAD⁺ levels, therapy boosts mitochondrial energy, enhances metabolism, supports brain function, and helps cells repair and resist stress. These improvements translate into more energy, sharper focus, and greater resilience in everyday life.
Is NAD⁺ therapy safe?
Yes, clinical studies show NAD⁺ therapy and its precursors are generally safe and well-tolerated, with only mild and temporary side effects reported. When taken under professional supervision, it is considered a reliable and low-risk option for long-term health.
Who can benefit from NAD⁺ therapy?
Anyone experiencing fatigue, slow recovery, brain fog, or age-related decline may benefit, as well as those seeking anti-aging and longevity support. Athletes, professionals, and older adults often use it to optimize energy and maintain peak performance.
References:
Covarrubias, A. J., Perrone, R., Grozio, A., & Verdin, E. (2020). NAD⁺ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 22(2), 119–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00313-x
Rajman, L., Chwalek, K., & Sinclair, D. A. (2018). Therapeutic potential of NAD-boosting molecules: The in vivo evidence. Cell Metabolism, 27(3), 529–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.011
Conlon, N. J. (2022). The role of NAD⁺ in regenerative medicine. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 150(4 Suppl), 41S–48S. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000009673
Yusri, K., Jose, S., Vermeulen, K. S., Tan, T. C. M., & Sorrentino, V. (2025). The role of NAD⁺ metabolism and its modulation of mitochondria in aging and disease. npj Metabolic Health and Disease, 3, Article 26. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44324-025-00067-0
Shoji, M., Kato, H., Koshizaka, M., Kaneko, H., Baba, Y., Ishikawa, T., Teramoto, N., Kinoshita, D., Yamaguchi, A., Maeda, Y., Inaba, Y., Shiko, Y., Ozawa, Y., Bohr, V. A., Maezawa, Y., & Yokote, K. (2025). Nicotinamide riboside supplementation benefits in patients with Werner syndrome: A double-blind randomized crossover placebo-controlled trial. Aging Cell, 24(8), e70093. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.70093
Covarrubias, A. J., Perrone, R., Grozio, A., & Verdin, E. (2021). NAD⁺ metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 22(2), 119–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00313-x
Braidy, N., Villalva, M. D., & van Eeden, S. (2020). Sobriety and satiety: Is NAD⁺ the answer? Antioxidants, 9(5), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050425