Hi readers, we at Vita Bella hope you had a wonderful Thanksgiving weekend.
Infertility affects many couples, and in up to half of those cases, male factors contribute. Clomiphene citrate (CC), originally used by women for fertility, is also gaining attention for its ability to increase testosterone levels and potential to improve male fertility. Clinical evidence shows CC can enhance sperm parameters, and increase testosterone production.
At Vita Bella, we explore evidence-based solutions that truly make a difference. Discover how clomiphene citrate, a safe and effective oral therapy, restore hormonal balance, with the added benefit of potentially maintaining or improving their fertility.
What Is Clomiphene and Why Use It in Men?
Clomiphene 1 is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). In men, it works by blocking estrogen feedback at the pituitary, which increases the release of gonadotropins (LH, FSH) and stimulates endogenous testosterone production and spermatogenesis. This mechanism helps normalize hormonal balance in men with hypogonadism or idiopathic infertility.
What are Clinical Evidence and Human Trials related to Clomiphene citrate?
A meta-analysis 2 shows that clomiphene citrate increases sperm concentration and motility in infertile men, with a favorable safety profile. In a controlled prospective trial 3, CC improved sperm parameters vs placebo in infertile men.
Another trial 4 evaluated oligospermic men treated with 50 mg daily for 6–9 months: compared to control, the treated group saw statistically significant increases in sperm density, motility, and volume, and 7 pregnancies occurred in the treated vs none in controls.
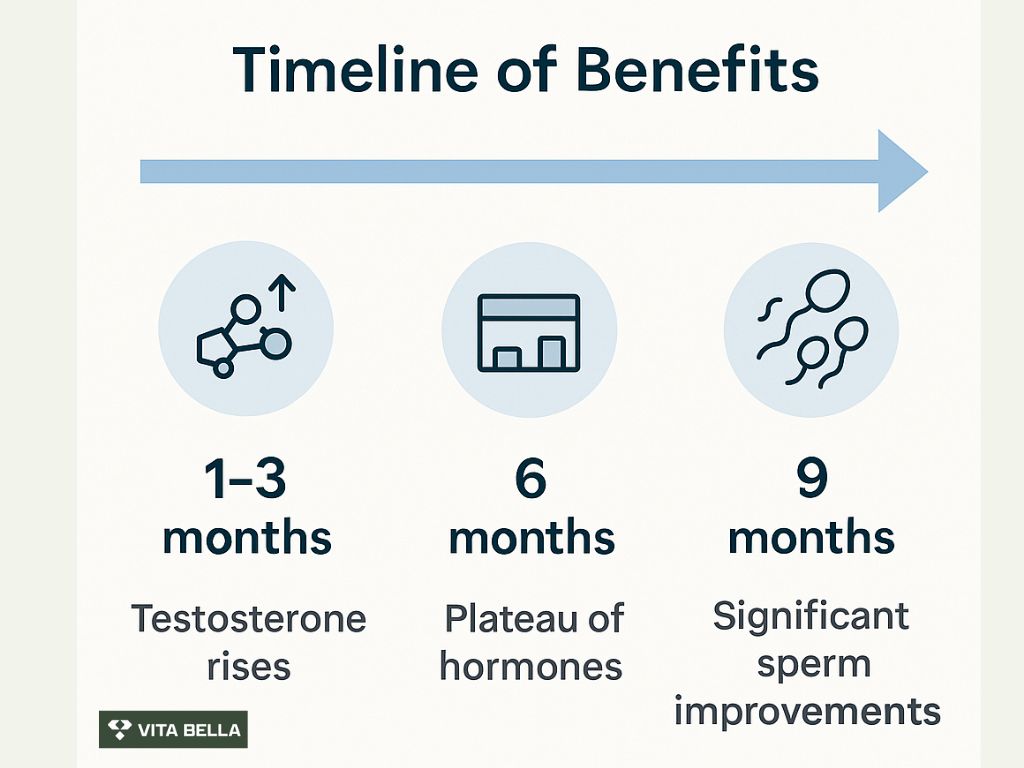
One study 5 in oligospermic men found that CC also raises serum testosterone levels alongside improvements in semen parameters. Over time, CC produces “temporal changes” in testosterone: the initial rise may plateau around 6 months, and sperm concentration benefits are more often noted after 9 months of use.
What are the Key Benefits and Advantages of Clomiphene citrate?
Clomiphene citrate restores more youthful testosterone levels with added benefit of potentially enhancing sperm count, motility, and semen volume. It’s an affordable, non-invasive oral treatment that offers men a safe and effective first-line option for hormone restoration
1- Hormonal Restoration
By blocking estrogen’s negative feedback at the hypothalamus, CC increases luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion. This rise stimulates the testes to produce endogenous testosterone and support spermatogenesis, unlike testosterone replacement therapy, which often suppresses sperm production. As a result, CC addresses low testosterone symptoms while still preserving fertility.
2- Improved Sperm Quality
Clomiphene citrate has been shown in multiple human studies 2 to improve sperm concentration, motility, and semen volume in infertile men. In a meta-analysis, men treated with CC experienced significant increases in total motile sperm count compared to placebo, providing a measurable improvement in fertility potential. This makes CC especially valuable in cases of idiopathic oligospermia where no structural abnormalities are found.
3- Pregnancy Outcomes
Ultimately, the goal of fertility treatment is pregnancy. In a controlled trial 4 of oligospermic men treated with CC 50 mg daily, 7 pregnancies occurred in the treatment group, compared to none in the control group. While results can vary, these outcomes highlight the clinical significance of improved sperm quality translating into real-world fertility success.
4- Oral, Low-Cost Option
Unlike testosterone or injectable gonadotropins CC is an inexpensive oral medication. Its cost-effectiveness makes it an accessible first-line therapy for men with low testosterone that also value maintaining fertility.
What is the optimal Use of Clomiphene citrate?
For best results, clomiphene citrate is typically used for 6–9 months, as improvements in testosterone levels as well as in sperm quality take time to appear. Regular monitoring of hormone levels andsemen parameters is essential, and it works most effectively when the reproductive hormonal axis is intact.
Baseline Hormonal Assessment: CC works best when baseline FSH, LH, and gonadal axis are intact (i.e. not severe primary testicular failure).
Monitoring: Regularly assess semen parameters, testosterone, estradiol, and gonadotropins.
Combination Therapies: Some data 6 show that combining CC with antioxidants (e.g. vitamin E) may further enhance outcomes.
What are the Cautions about Clomiphene citrate?
Hormonal balance must be monitored; excessive estrogen rise (via aromatization) is a possible risk. It is not a magic solution; success depends on underlying pathology, partner fertility, and lifestyle factors.
Not all studies 7 uniformly show a fertility benefit; some reviews call the evidence insufficient to guarantee fertility restoration.CC is less effective in men with severely impaired testicular function or obstructive azoospermia.
Turning Infertility Struggles into Fertility Success with Vita Bella
For many couples, infertility is a heavy burden, and low sperm quality in men is often at the core. Instead of invasive and costly treatments, Vita Bella introduces an affordable and effective therapy: clomiphene citrate. Backed by clinical evidence, it’s helping men regain hormonal balance and potentially maintain or improve fertility outcomes. With patience and the proper guidance, even long-standing struggles can see a breakthrough. At Vita Bella, we’re committed to turning challenges into hopeful journeys toward parenthood.
FAQs
How does clomiphene citrate work in men?
Clomiphene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). In men, it blocks estrogen’s negative feedback at the brain level, stimulating the release of LH and FSH. This triggers the testes to produce more testosterone and support sperm production.
How long does it take for clomiphene citrate to improve sperm quality?
Improvements in testosterone can appear within 1–3 months, but noticeable changes in sperm concentration and motility often take 6–9 months. Patience and consistent monitoring are essential.
Is clomiphene citrate safe for men?
Yes, clinical trials show clomiphene has a favorable safety profile when prescribed under medical supervision. Side effects are usually mild and may include mood changes, visual disturbances, or gynecomastia, but most men tolerate it well.
Can clomiphene citrate alone improve fertility?
Not always, while CC can significantly improve sperm count and quality, pregnancy success also depends on the partner’s fertility and other health factors. Some men may need combination therapy or assisted reproductive techniques for optimal results.
References:
Huijben, M., Huijsmans, R. L. N., Lock, M. T. W., de Kemp, V. F., de Kort, L. M. O., & van Breda, J. H. M. K. (2023). Clomiphene citrate for male infertility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Andrology, 11(6), 987–996. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36680549/
Shukla, J., Moni, S. N., Hasan, M. M., Islam, M. A., Shikha, A. N., Jahan, N.-W.-B., & Ishrat, S. (2025). Clomiphene citrate improves sperm parameters in infertile men with idiopathic oligoasthenozoospermia. Clinical and Experimental Reproductive Medicine, 52(3), 252–258. https://doi.org/10.5653/cerm.2024.07353
Mićić, S., & Dotlić, R. (1985). Evaluation of sperm parameters in clinical trial with clomiphene citrate of oligospermic men. The Journal of Urology, 133(2), 221–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)48889-6
Panner Selvam, M. K., Baskaran, S., Tannenbaum, J., Greenberg, J., Shalaby, H. Y., Hellstrom, W. J. G., & Sikka, S. C. (2023). Clomiphene Citrate in the Management of Infertility in Oligospermic Obese Men with Hypogonadism: Retrospective Pilot Study. Medicina, 59(11), 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59111902
Ghanem, H., Shaeer, O., & El-Segini, A. (2010). Combination clomiphene citrate and antioxidant therapy for idiopathic male infertility: A randomized controlled trial. Fertility and Sterility, 93(7), 2232–2235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-0282(09)00236-2
Willets, A. E., Corbo, J. M., & Brown, J. N. (2013). Clomiphene for the treatment of male infertility. Reproductive Sciences, 20(7), 739–744. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719112466304





















