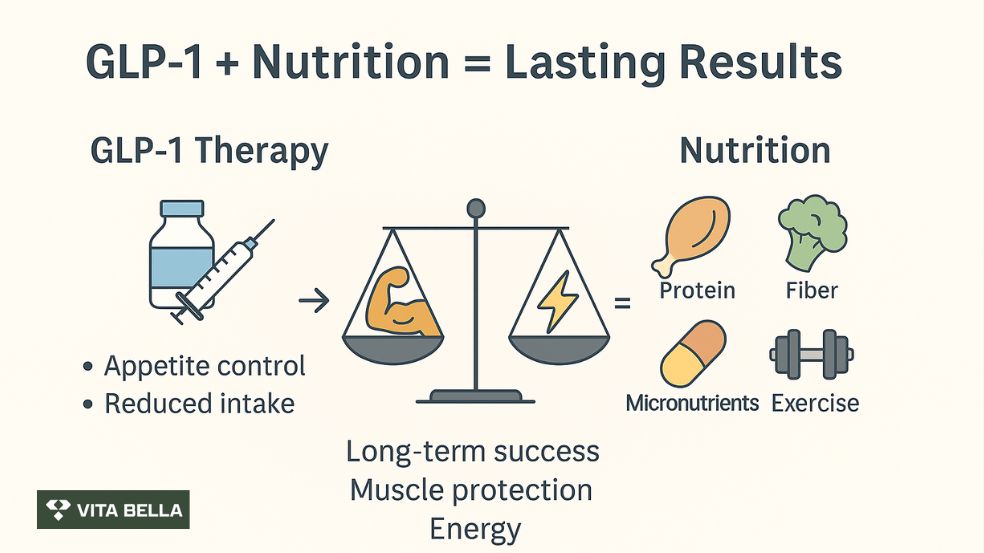
The key to unlocking the full power of GLP-1 therapy isn’t just the medication but the food you eat alongside it. Pairing GLP-1 therapy with the right foods can optimize receptor response and enhance overall outcomes. GLP-1 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) are transforming the management of obesity and metabolic health. They reduce appetite, slow gastric emptying, and lower calorie intake, producing meaningful weight loss in clinical settings.
However, nutrition plays an essential role in maintaining these benefits, protecting muscle mass, and ensuring long-term success. GLP-1 therapy with Semaglutide is powerful, but without the proper nutrition, results can fade into fatigue, muscle loss, or nutrient gaps. At Vita Bella, we combine medical insight with tailored nutritional guidance to help you maximize weight loss, protect your health, and feel your best every day. Start your transformation with support that lasts.
Why Nutrition Matters with GLP-1 Therapy?
Nutrition matters with GLP-1 therapy because it preserves muscle, prevents deficiencies, and makes weight loss sustainable. Studies 1 show GLP-1 RAs can produce 5–18% placebo-adjusted weight reduction in clinical trials. Yet, real-world outcomes are often smaller due to poor adherence and a lack of supportive nutrition guidance.
According to a study 2, nutritional guidance ensures that weight loss is healthy, sustainable, and protective against muscle and bone loss. Without adequate protein and micronutrient intake, patients risk fatigue, lean mass decline, and metabolic rebound.
How GLP-1 Affects Eating Patterns?
GLP-1 medications suppress appetite and enhance satiety, which helps patients consume fewer calories naturally. In real practice, many users reduce their daily intake depending on dose and duration. This calorie reduction means every bite must count. Food choices should emphasize nutrient density and balance:
Lean proteins (chicken, fish, legumes)
Fiber-rich vegetables and whole grains
Healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and olive oil
Limited intake of processed foods and sugary snacks.
These patterns not only complement GLP-1 action 3 but also support gut health and reduce GI side effects.
Core Nutritional Strategies with GLP-1:
A structured nutrition plan is essential to maximize the benefits of GLP-1 therapy. Prioritizing protein, fibre-rich foods, micronutrient balance, and resistance training helps preserve muscle, improve tolerance, and support long-term weight management.
1- Prioritize Protein:
Protein intake of 1.2–1.6 g/kg/day is recommended to preserve lean body mass during weight loss. Adequate protein helps maintain muscle strength, metabolic rate, and satiety, all of which can decline during calorie restriction. Lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, eggs, and legumes are ideal for balancing nutrition with reduced appetite.
2- Eat Small, Balanced Meals
GLP-1 therapy slows gastric emptying, which can lead to nausea, bloating, or discomfort when meals are too large. Smaller, more frequent meals allow smoother di0.gestion and help patients meet nutrient needs without overwhelming the gut. Balanced meals should include moderate protein, complex carbs, and healthy fats to optimize tolerance and nutrient absorption.
3- Boost Fiber Intake
Inclusion of fiber-fortified bar (12.7 g fiber) increased GLP-1 secretion and reduced total energy intake in healthy adults. In a controlled human trial 4 , illustrating fibers role in satiety and hormonal modulation.
4- Manage Micronutrients
With reduced overall calorie intake, patients risk deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, calcium, iron, and B12. Research 5 explains that regular monitoring through lab work and supplementation, when needed, ensures that these key nutrients remain at healthy levels. Maintaining micronutrient balance supports bone strength, red blood cell production, and long-term metabolic health.
5- Combine with Resistance Training.
Nutrition alone is not enough to maintain muscle mass while losing weight. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, prevents lean tissue loss and improves metabolic outcomes. When paired with sufficient protein intake, strength training ensures weight loss is primarily fat, while preserving bone density and functional strength.
Common Challenges and Solutions
GLP-1 therapy often causes gastrointestinal discomfort, lean muscle loss, and nutrient gaps when calorie intake drops. These challenges can be minimized with small, balanced meals, higher protein intake, resistance training, and targeted micronutrient monitoring.
Gastrointestinal Side Effects: Nausea, diarrhea, and delayed digestion are frequent early in GLP-1 therapy. Dieticians recommend gradual dietary adjustments, softer foods, and reduced fat intake to improve tolerance.
Risk of Muscle Loss: Without high-quality protein and resistance training, GLP-1 users may lose lean tissue along with fat mass. Structured nutrition plans protect muscle strength and long-term weight stability.
Knowledge Gaps in Care: A recent study 3 found that many clinicians feel underprepared to give dietary advice to GLP-1 users. Patients often lack proper guidance, which reduces adherence and outcomes.
Evidence-Based Dietary Patterns for GLP-1 Users
A diet rich in vegetables, legumes, fish, and olive oil, this pattern enhances cardiometabolic outcomes and improves satiety signals. It has been shown that specific eating patterns synergize with GLP-1 therapy:
Recent guidance 1 emphasizes that a Mediterranean-style diet and meals enriched in protein or fiber may enhance GLP-1 secretion and complement GLP-1 therapy, supporting satiety and metabolic benefits.
Moreover, protein intake that exceeds the standard RDA is recommended to preserve lean body mass during GLP-1–aided weight loss, as suggested by the study 6
Redefine Success on GLP-1 with Vita Bella.
What does success mean, just losing weight, or gaining lasting health? Too many patients stop at the scale and miss the bigger picture. Vita Bella helps you redefine success by aligning Semaglutide (GLP-1 therapy) with nutrition. Our strategies preserve strength, prevent deficiencies, and extend your results. We transform side effects into opportunities for smarter, healthier eating. With Vita Bella, success isn’t temporary; it’s a new way of living.
FAQs:
Why is nutrition important when using GLP-1 therapy?
Nutrition ensures that weight loss from GLP-1 therapy is healthy and sustainable. It helps prevent muscle loss, nutrient deficiencies, and rebound weight gain, while also improving tolerance to treatment.
What foods should I prioritize while on GLP-1 medication?
Focus on lean proteins, fibre-rich vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, and healthy fats. These foods preserve muscle, enhance satiety, and provide essential vitamins and minerals during reduced calorie intake.
Can GLP-1 therapy cause nutrient deficiencies?
Yes, because GLP-1 therapy lowers appetite and food intake, deficiencies in vitamin D, B12, iron, and calcium can occur without careful planning. Regular monitoring and supplementation help maintain optimal levels.
How can I reduce side effects like nausea while on GLP-1 therapy?
Eating smaller, balanced meals, avoiding high-fat or greasy foods, and staying hydrated can reduce nausea and bloating. Gradual dietary adjustments make therapy easier to tolerate.
References:
Gofron, K. K., Wasilewski, A., & Małgorzewicz, S. (2025). Effects of GLP-1 analogues and agonists on the gut microbiota: A systematic review. Nutrients, 17(8), 1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081303
Fitch, A., Gigliotti, L., & Bays, H. E. (2025). Application of nutrition interventions with GLP-1 based therapies: A narrative review of the challenges and solutions. Metabolism Open, 25, 100688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metop.2025.100688





















