Feeling exhausted, unfocused, or not quite yourself lately? These subtle shifts might not just be aging; they could be early warning signs of low testosterone that most men overlook. Low testosterone 1, also known as male hypogonadism or testosterone deficiency, occurs when serum testosterone levels fall below clinical thresholds and symptoms emerge. In men, low T impairs energy, mood, libido, muscle mass, and long-term health.
You don’t have to accept fatigue, low libido, or mental fog as a regular part of aging. Vita Bella’s medically guided TRT programs are designed to restore balance, boost performance, and renew energy. Learn how addressing low testosterone early can help you feel powerful, focused, and in control again.
Why Low Testosterone Often Goes Undetected?
Recognizing low testosterone symptoms early can prevent compounding issues. Many men dismiss subtle signs, allowing dysfunction to worsen. By understanding these indicators and seeking evaluation, you can mitigate risks and restore energy.
A review 2 explains that testosterone levels gradually decline with age, on average, about 1% per year after age 30. Population studies 3 estimate that 6–12% of middle-aged to older men have symptomatic hypogonadism. Because the onset is gradual and symptoms overlap with aging or stress, many men normalize fatigue, mood drift, or libido decline, delaying diagnosis and intervention.
What are the Early Symptoms of Low Testosterone that most Men Overlook?
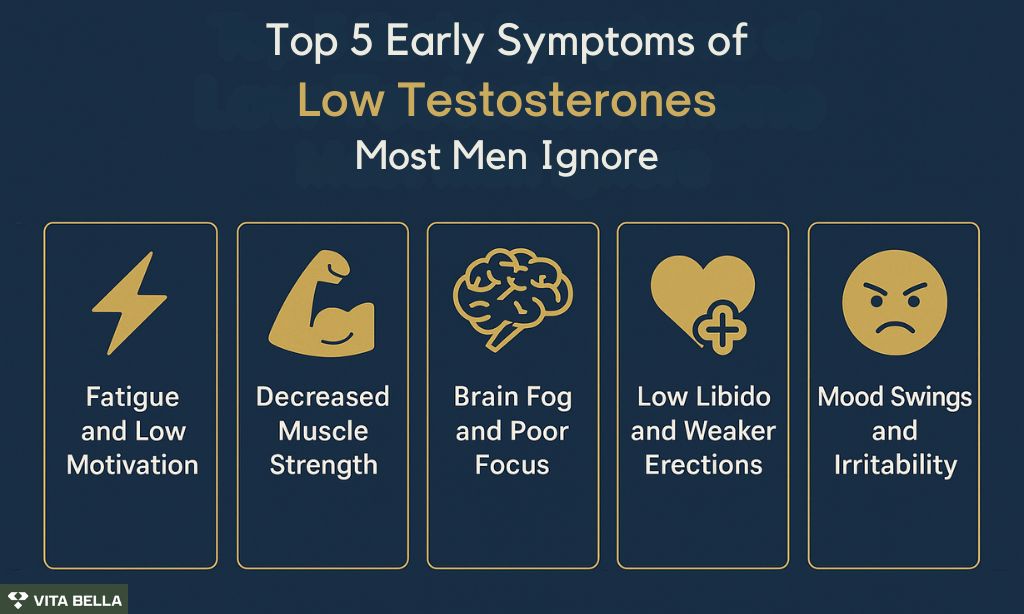
Many men dismiss the early signs of low testosterone as simple aging or stress, but these subtle symptoms often appear long before hormone levels drop severely. Persistent fatigue, reduced motivation, mood swings, and a noticeable dip in libido can all signal early testosterone deficiency.
Fatigue and low motivation: You may feel exhausted despite adequate sleep, and your drive to perform daily tasks wanes.
Loss of muscle strength: You might struggle to keep up with weights or notice strength decreasing even with consistent workouts.
Brain fog and poor concentration: Forgetfulness, slower thinking, or difficulty focusing are early cognitive signs.
Reduced libido and weaker erections: Desire often fades before performance; erections may be less firm or frequent.
Mood swings and irritability: You may experience fluctuations in mood, increased irritability, or low emotional resilience.
What are Physical Changes That Signal Low Testosterone?
Since physical changes evolve gradually, many men don’t connect them to hormone deficiency until more overt problems appear.
Shrinking testicles & reduced hair growth: Testicular volume decline and thinning of facial, body, or pubic hair may occur progressively.
Increased body fat & gynecomastia: Testosterone decline often leads to fat gain around the abdomen or chest, sometimes causing mild breast tissue enlargement.
Hot flashes or temperature sensitivity: Though less common, some men report episodic flushing or intolerance to heat as hormone levels fluctuate.
What are Emotional and Cognitive Symptoms of Low Testosterone?
Depression, apathy, and a diminished sense of purpose often accompany low T. Memory lapses or mental fatigue may emerge as well.
Moreover, human studies 4 suggest associations between lower testosterone and reduced cognitive performance, particularly in executive function and verbal memory tasks. As a result, many men misattribute mood or cognitive decline to aging or stress, rather than a hormonal imbalance.
What are the Long-Term Health Risks of Ignoring Low T
1- Bone density loss, higher fracture risk
Research 2 shows that men with low testosterone have an increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures over time.
2- Increased abdominal fat, metabolic syndrome and diabetes
Testosterone deficiency favors central fat accumulation, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia.
3- Possible modulation cardiovascular disease progression
Although the relationship is complex and still under study 1, hypogonadism is often linked to worse cardiovascular risk profiles in observational cohorts. Ignoring low T can thus contribute to a cascade of worsening metabolic and skeletal dysfunction.
When to See a Doctor for Low Testosterone?
If symptoms persist for more than 2–4 weeks and interfere with quality of life, you should seek evaluation. Clinically 5, a total testosterone below ~300 ng/dL (measured in the morning on two occasions) is a standard benchmark for deficiency, particularly when symptoms align. Ask your provider for a hormone panel including total testosterone, free testosterone, LH/FSH, estradiol, hematocrit, lipid panel, and PSA.
What are the Treatment Options for Low Testosterone?
1. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
When properly supervised, Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) effectively restores hormone balance in men with confirmed hypogonadism. Human studies 1 demonstrate significant improvements in sexual desire, muscle strength, mood stability, and bone density within 3–6 months of consistent therapy.
TRT works by maintaining serum testosterone within the physiological range, which supports red blood cell production, lean mass development, and cognitive performance. Modern delivery options, such as injections and creams, allow physicians to tailor therapy precisely.
Furthermore, research confirms that when monitored carefully (checking hematocrit, estradiol, and PSA), TRT maintains a strong safety profile, with no significant increase in cardiovascular or prostate risk in appropriately selected patients.
2. Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle optimization remains a cornerstone of hormonal health, both independently and alongside TRT. Regular resistance and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) increase testosterone and growth hormone secretion while reducing fat mass. Clinical trials show that sedentary men can experience a 15–20% rise in total testosterone after adopting consistent strength training programs.
Reducing visceral fat improves insulin sensitivity, which directly supports natural testosterone production. Moreover, sleeping 7–9 hours per night is vital; one week of sleep restriction (5 hours/night) decreased testosterone levels by up to 10–15% in healthy young men. Consistent training, balanced nutrition, and proper recovery complement medical interventions and may reduce the need for higher TRT doses over time.
What are the Medical Monitoring and Follow-Up requirements for Low Testosterone?
Research 5 shows that regular lab monitoring is crucial for safe, effective outcomes. Physicians typically re-evaluate testosterone, estradiol, hematocrit, and lipid profiles every 3–6 months. These follow-ups ensure optimal dosing and help avoid complications like polycythemia or hormone imbalance.
How Vita Bella Can Help with Low Testosterone?
At Vita Bella, we deliver personalized TRT programs backed by medical oversight, advanced diagnostics, and continuous monitoring. We guide you from initial evaluation and lab review through dose optimization and symptom tracking. Partnering with us means you won’t face low T alone. Let’s get ahead of the decline. Book your consultation with Vita Bella and start recognizing rather than ignoring the signs that matter.
From Exhausted to Energized - Restore Your Energy Now with Vita Bella
Low testosterone can make you feel like a shadow of your former self less drive, less focus, less confidence. At Vita Bella, we specialize in restoring optimal hormone levels through personalized TRT programs, helping you regain energy, motivation, and performance from the inside out.
FAQs
Can low testosterone cause fatigue and low motivation?
Yes, low testosterone directly impacts energy metabolism and dopamine levels, leading to constant tiredness and lack of drive. When untreated, this can progressively lower productivity, mood, and overall quality of life. Over time, it may also contribute to weight gain and decreased muscle strength, further worsening fatigue and motivation levels.
Is low testosterone a regular part of aging?
Yes, but not always acceptable. Testosterone naturally declines about 1% per year after age 30, but severe drops aren’t “normal aging.” With proper evaluation and therapy, men can maintain healthy energy, libido, and performance well into later life.
Can testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) safely restore energy and libido?
Yes, under medical supervision, TRT effectively enhances mood, stamina, and sexual function by restoring optimal hormone levels. Regular monitoring ensures safety and allows fine-tuning for the best long-term outcomes.
Should I see a doctor if I have symptoms but haven’t tested my testosterone yet?
Yes, persistent symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, or reduced libido warrant a professional hormone assessment. Early testing can confirm testosterone deficiency and prevent complications from long-term imbalance.
References:
Bhasin, S., & Snyder, P. J. (2025, August 7). Testosterone treatment in middle-aged and older men with hypogonadism. The New England Journal of Medicine, 393(6), 581–591. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra2404637
Munari, E. V. (2024). The complications of male hypogonadism: Is it just a matter of low testosterone? Frontiers in Reproductive Health, 6, 1423395. https://doi.org/10.3389/frph.2024.1423395
Julius, D. (2022). Management of male fertility in hypogonadal patients on testosterone replacement therapy. Urology Case Reports, 46, 102279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eucr.2022.102279
Sargis, R. M., & Andrew, R. (2023). Evaluation and treatment of male hypogonadism. Medscape. Retrieved from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/922038-overview
Heidelbaugh, J. J., & Belakovskiy, A. (2022). Testosterone replacement therapy for male hypogonadism. American Family Physician, 105(3), 271–278. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2022/0300/p271.html